Authentication
Maraboo API uses HMAC-SHA256 authentication to ensure secure access to your resources. This guide explains how authentication works and how to properly authenticate your API requests.
Overview
All API requests to Maraboo must be authenticated using an API token with HMAC-SHA256 signature. This ensures that:
- Requests are coming from verified sources
- Data integrity is maintained during transmission
- Unauthorized access is prevented
Required Headers
Every API request must include the following headers:
Authorization: HMAC-SHA256 YOUR_PUBLIC_KEY:YOUR_PRIVATE_KEY
X-Origin: third-party-api.mara.boo
X-Timestamp: 2025-10-11T21:30:00.000Z
Content-Type: application/jsonHeader Descriptions
| Header | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Authorization | HMAC-SHA256 PUBLIC_KEY:PRIVATE_KEY | API key pair (public and private keys) with HMAC-SHA256 prefix |
| X-Origin | third-party-api.mara.boo | Required origin identifier for all third-party API requests |
| X-Timestamp | Current timestamp (ISO 8601) | Current time in ISO 8601 format (e.g., 2025-10-11T21:30:00.000Z) |
| Content-Type | application/json | Request content type |
Important
All three headers (Authorization, X-Origin, and X-Timestamp) are mandatory for all requests. Requests missing any of these headers will be rejected with a 401 Unauthorized or 403 Forbidden response.
How API Authentication Works
Maraboo uses a Service Account and API Key system for authentication:
Step 1: Create a Service Account
Service Accounts provide scoped access for automated systems and integrations.
To create a Service Account:
- Log in to the Business Portal
- Navigate to Developers > Service Accounts
- Click "Create Service Account"
- Provide a name and description for the service account
- Save the service account
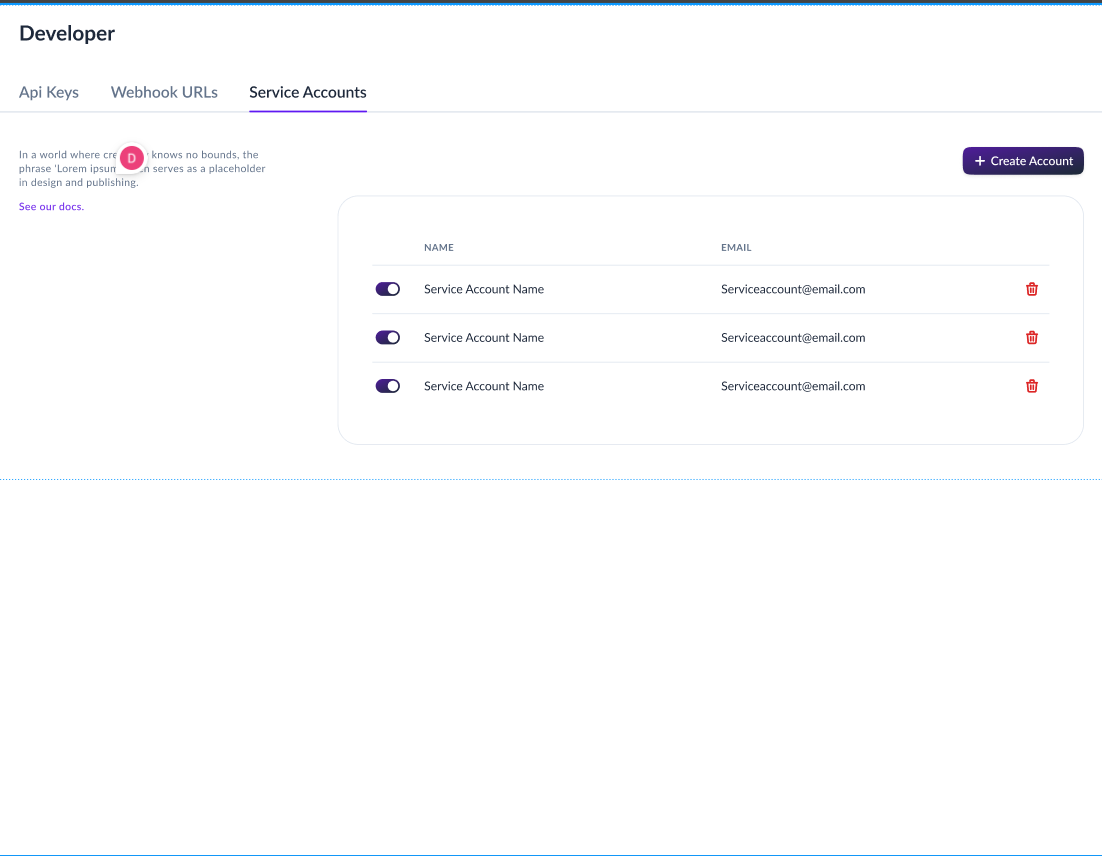
Service Account Features:
- Separate credentials per service/application
- Can be disabled without affecting other services
- Supports multiple API keys (one active key at a time)
Step 2: Generate API Keys for the Service Account
Once you have a service account, you need to generate an API key pair.
To generate API Keys:
- Navigate to Developers > API Keys
- Select the service account you created
- Click "Generate API Key"
- Both the Public Key and Private Key will be displayed
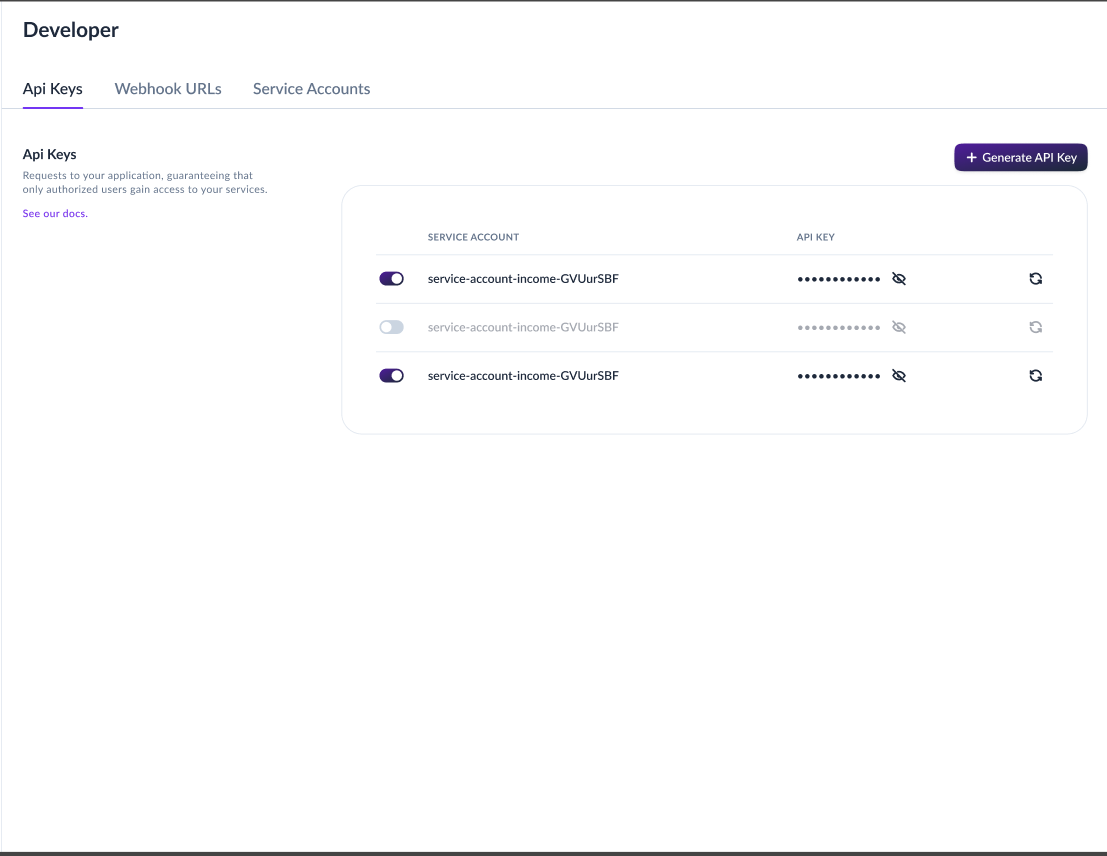
Save Your Keys Immediately!
The Private Key will only be shown ONCE during generation. You must save both keys securely at this time, as you won't be able to view the private key again. If you lose the private key, you'll need to regenerate a new key pair.
API Key Characteristics:
- One active key per service account at any given time
- Public/Private key pair (both required for authentication)
- Keys can be regenerated when needed
- Keys can be revoked immediately if compromised
- Private key is only shown once upon creation
Step 3: Use API Keys in Your Requests
Include your API key pair in every request using the Authorization header:
Authorization: HMAC-SHA256 YOUR_PUBLIC_KEY:YOUR_PRIVATE_KEYThe format is: HMAC-SHA256 followed by your public key and private key separated by a colon (:).
HMAC-SHA256 Authentication
What is HMAC-SHA256?
HMAC (Hash-based Message Authentication Code) with SHA-256 is a cryptographic authentication method. In Maraboo's implementation:
- HMAC-SHA256 is the authentication scheme identifier
- Your API keys (public and private key pair) serve as the authentication credentials
- The keys ensure requests are coming from verified sources
- The timestamp header prevents replay attacks
How It Works
- Create Service Account: Set up a service account with appropriate permissions
- Generate API Key Pair: Create public and private keys for the service account
- Include Keys in Header: Add both keys to the
Authorizationheader in formatHMAC-SHA256 PUBLIC_KEY:PRIVATE_KEY - Add Timestamp: Include current ISO 8601 timestamp in
X-Timestampheader - Add Origin: Include
third-party-api.mara.booinX-Originheader - Send Request: Make the API request with all required headers
- Server Validates: Maraboo verifies the key pair and timestamp
TIP
All three headers (Authorization, X-Origin, and X-Timestamp) must be present in every request. See the Code Examples section below for language-specific implementations.
API Key Lifecycle
Key Generation
API keys are generated through the Business Portal when you create them for a service account.
Steps to generate API keys:
- Log in to the Business Portal
- Create or select a service account at Developers > Service Accounts
- Navigate to Developers > API Keys
- Generate a new API key for your service account
- Immediately save both the public and private keys (private key won't be shown again)
Key Storage
Security Best Practice
Never hardcode API keys in your source code or commit them to version control. Both the public and private keys should be stored securely.
Recommended storage methods:
- Environment Variables: Store keys in
.envfiles (excluded from version control) - Secret Management Services: Use AWS Secrets Manager, Azure Key Vault, HashiCorp Vault, etc.
- Configuration Management: Use secure configuration management tools
Example - Environment Variables:
# .env file (never commit this file)
MARABOO_PUBLIC_KEY=your_public_key_here
MARABOO_PRIVATE_KEY=your_private_key_here
MARABOO_API_URL=https://gateway.mara.booKey Expiry and Rotation
API keys must be rotated periodically to maintain security.
Key Expiry:
- Keys must be rotated regularly (rotation period: TBD)
- You will receive email notifications before your keys expire
- Expired keys will stop working and must be regenerated
Key Rotation Process:
- Generate a new API key for your service account in the Business Portal
- Save the new keys (public and private) immediately
- Update your application with the new key pair
- Test thoroughly in your staging/sandbox environment
- Deploy to production with the new keys
- Revoke the old key after successful deployment and verification
Rotation Best Practices
Rotate API keys:
- ✅ Before the expiry notification deadline
- ✅ Immediately if a key is compromised or exposed
- ✅ When an employee with key access leaves the organization
- ✅ After a security incident
- ✅ As part of regular security audits
Important: Since each service account can only have one active key at a time, ensure your rotation process is smooth to avoid service interruptions.
Key Regeneration
If you lose your private key or need to rotate keys, you can regenerate them:
- Navigate to Developers > API Keys
- Select your service account
- Click "the regenerate icon"
- The old key pair will be revoked
- A new public and private key pair will be generated
- Save both keys immediately (private key won't be shown again)
Service Disruption
Regenerating keys will immediately revoke the old key pair. Ensure you have a plan to update all services using the old keys to prevent disruptions.
Key Revocation
You can revoke API keys at any time if they're compromised or no longer needed:
- Navigate to Developers > API Keys
- Select the service account
- Click "toggle the service account and api key off."
- The key pair will be immediately invalidated
- All requests using the revoked keys will fail
When to revoke keys:
- Keys have been exposed or compromised
- Service account is no longer in use
- Employee with key access has left
- As part of security incident response
Code Examples
Here are examples of how to authenticate and make API requests in different programming languages:
const MARABOO_PUBLIC_KEY = process.env.MARABOO_PUBLIC_KEY;
const MARABOO_PRIVATE_KEY = process.env.MARABOO_PRIVATE_KEY;
const BASE_URL = 'https://gateway.mara.boo';
async function getWallets() {
// Generate current timestamp in ISO 8601 format
const timestamp = new Date().toISOString();
const response = await fetch(`${BASE_URL}/api-access/purses/wallets`, {
method: 'GET',
headers: {
'Authorization': `HMAC-SHA256 ${MARABOO_PUBLIC_KEY}:${MARABOO_PRIVATE_KEY}`,
'X-Origin': 'third-party-api.mara.boo',
'X-Timestamp': timestamp,
'Content-Type': 'application/json'
}
});
if (!response.ok) {
throw new Error(`API request failed: ${response.status}`);
}
return await response.json();
}
// Usage
try {
const wallets = await getWallets();
console.log('Wallets:', wallets);
} catch (error) {
console.error('Error fetching wallets:', error);
}import os
import requests
from datetime import datetime, timezone
MARABOO_PUBLIC_KEY = os.getenv('MARABOO_PUBLIC_KEY')
MARABOO_PRIVATE_KEY = os.getenv('MARABOO_PRIVATE_KEY')
BASE_URL = 'https://gateway.mara.boo'
def get_wallets():
"""Fetch all wallets for the authenticated business."""
# Generate current timestamp in ISO 8601 format
timestamp = datetime.now(timezone.utc).isoformat()
headers = {
'Authorization': f'HMAC-SHA256 {MARABOO_PUBLIC_KEY}:{MARABOO_PRIVATE_KEY}',
'X-Origin': 'third-party-api.mara.boo',
'X-Timestamp': timestamp,
'Content-Type': 'application/json'
}
response = requests.get(
f'{BASE_URL}/api-access/purses/wallets',
headers=headers
)
response.raise_for_status()
return response.json()
# Usage
try:
wallets = get_wallets()
print('Wallets:', wallets)
except requests.exceptions.RequestException as error:
print(f'Error fetching wallets: {error}')import java.net.URI;
import java.net.http.HttpClient;
import java.net.http.HttpRequest;
import java.net.http.HttpResponse;
import java.time.Instant;
public class MarabooClient {
private static final String MARABOO_PUBLIC_KEY = System.getenv("MARABOO_PUBLIC_KEY");
private static final String MARABOO_PRIVATE_KEY = System.getenv("MARABOO_PRIVATE_KEY");
private static final String BASE_URL = "https://gateway.mara.boo";
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
HttpClient client = HttpClient.newHttpClient();
// Generate current timestamp in ISO 8601 format
String timestamp = Instant.now().toString();
// Format: HMAC-SHA256 PUBLIC_KEY:PRIVATE_KEY
String authHeader = "HMAC-SHA256 " + MARABOO_PUBLIC_KEY + ":" + MARABOO_PRIVATE_KEY;
HttpRequest request = HttpRequest.newBuilder()
.uri(URI.create(BASE_URL + "/api-access/purses/wallets"))
.header("Authorization", authHeader)
.header("X-Origin", "third-party-api.mara.boo")
.header("X-Timestamp", timestamp)
.header("Content-Type", "application/json")
.GET()
.build();
HttpResponse<String> response = client.send(request,
HttpResponse.BodyHandlers.ofString());
if (response.statusCode() == 200) {
System.out.println("Wallets: " + response.body());
} else {
System.err.println("Error: " + response.statusCode());
}
}
}using System;
using System.Net.Http;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
public class MarabooClient
{
private static readonly string MARABOO_PUBLIC_KEY = Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("MARABOO_PUBLIC_KEY");
private static readonly string MARABOO_PRIVATE_KEY = Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("MARABOO_PRIVATE_KEY");
private static readonly string BASE_URL = "https://gateway.mara.boo";
public static async Task Main(string[] args)
{
using var client = new HttpClient();
// Generate current timestamp in ISO 8601 format
string timestamp = DateTime.UtcNow.ToString("o");
// Set up headers
client.DefaultRequestHeaders.Add("Authorization",
$"HMAC-SHA256 {MARABOO_PUBLIC_KEY}:{MARABOO_PRIVATE_KEY}");
client.DefaultRequestHeaders.Add("X-Origin", "third-party-api.mara.boo");
client.DefaultRequestHeaders.Add("X-Timestamp", timestamp);
client.DefaultRequestHeaders.Add("Content-Type", "application/json");
try
{
var response = await client.GetAsync($"{BASE_URL}/api-access/purses/wallets");
response.EnsureSuccessStatusCode();
string responseBody = await response.Content.ReadAsStringAsync();
Console.WriteLine($"Wallets: {responseBody}");
}
catch (HttpRequestException e)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Error fetching wallets: {e.Message}");
}
}
}package main
import (
"fmt"
"io"
"net/http"
"os"
"time"
)
func main() {
publicKey := os.Getenv("MARABOO_PUBLIC_KEY")
privateKey := os.Getenv("MARABOO_PRIVATE_KEY")
baseURL := "https://gateway.mara.boo"
// Generate current timestamp in ISO 8601 format
timestamp := time.Now().UTC().Format(time.RFC3339Nano)
// Create request
req, err := http.NewRequest("GET", baseURL+"/api-access/purses/wallets", nil)
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("Error creating request: %v\n", err)
return
}
// Set headers
req.Header.Set("Authorization", fmt.Sprintf("HMAC-SHA256 %s:%s", publicKey, privateKey))
req.Header.Set("X-Origin", "third-party-api.mara.boo")
req.Header.Set("X-Timestamp", timestamp)
req.Header.Set("Content-Type", "application/json")
// Send request
client := &http.Client{}
resp, err := client.Do(req)
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("Error fetching wallets: %v\n", err)
return
}
defer resp.Body.Close()
// Read response
body, err := io.ReadAll(resp.Body)
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("Error reading response: %v\n", err)
return
}
fmt.Printf("Wallets: %s\n", string(body))
}#!/bin/bash
MARABOO_PUBLIC_KEY="${MARABOO_PUBLIC_KEY}"
MARABOO_PRIVATE_KEY="${MARABOO_PRIVATE_KEY}"
BASE_URL="https://gateway.mara.boo"
# Generate current timestamp in ISO 8601 format
TIMESTAMP=$(date -u +"%Y-%m-%dT%H:%M:%S.%3NZ")
# Get Wallets
curl -X GET "${BASE_URL}/api-access/purses/wallets" \
-H "Authorization: HMAC-SHA256 ${MARABOO_PUBLIC_KEY}:${MARABOO_PRIVATE_KEY}" \
-H "X-Origin: third-party-api.mara.boo" \
-H "X-Timestamp: ${TIMESTAMP}" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json"Error Handling
Common Authentication Errors
| Status Code | Error | Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|---|
| 401 Unauthorized | Invalid or missing authentication | Token is invalid, expired, or missing | Verify token is correct and included in header |
| 403 Forbidden | Missing X-Origin header | Required X-Origin header not included | Add X-Origin: third-party-api.mara.boo to all requests |
| 403 Forbidden | Insufficient permissions | Token doesn't have required permissions | Check service account permissions in portal |
| 429 Too Many Requests | Rate limit exceeded | Too many requests in short time | Implement exponential backoff retry logic |
Example Error Response
{
"success": false,
"message": "Authentication failed",
"detail": "Invalid or missing authorization header",
"error_code": "AUTH_001"
}Security Best Practices
1. Secure Token Storage
- ✅ Store tokens in environment variables or secret management systems
- ✅ Use secure configuration management
- ❌ Never hardcode tokens in source code
- ❌ Never commit tokens to version control
2. Use HTTPS Only
- ✅ Always use
https://for API requests - ❌ Never send tokens over unencrypted
http://connections
3. Implement Token Rotation
- ✅ Rotate tokens regularly (every 90 days minimum)
- ✅ Have a process for emergency rotation
- ✅ Test new tokens before revoking old ones
4. Separate Service Accounts
- ✅ Create separate service accounts for different services/applications
- ✅ Regularly audit and remove unused service accounts
- ✅ Disable service accounts immediately when no longer needed
5. Monitor and Log
- ✅ Monitor API usage for unusual patterns
- ✅ Log authentication failures
- ✅ Set up alerts for suspicious activity
- ❌ Never log full API tokens
6. IP Whitelisting
- ✅ Provide your server IP addresses during API access request
- ✅ Update whitelisted IPs when infrastructure changes
- ✅ Use static IPs for production services
7. Emergency Response Plan
Have a plan for when keys are compromised:
Immediate actions:
- 🔴 Revoke the compromised key immediately
- 🔴 Regenerate a new key pair
- 🔴 Update all services with new keys
- 🔴 Monitor for unauthorized access attempts
- 🔴 Investigate how the key was exposed
- 🔴 Document the incident and response
Testing Authentication
Sandbox Environment
Test your authentication setup in the sandbox environment before going to production:
// Use sandbox URL for testing
const BASE_URL = 'https://sandbox-gateway.mara.boo';
// Use sandbox API token
const SANDBOX_TOKEN = process.env.MARABOO_SANDBOX_TOKEN;Verify Authentication
Use the Get Wallets endpoint as a simple authentication test:
# Generate timestamp
TIMESTAMP=$(date -u +"%Y-%m-%dT%H:%M:%S.%3NZ")
curl -X GET https://sandbox-gateway.mara.boo/api-access/purses/wallets \
-H "Authorization: HMAC-SHA256 ${SANDBOX_PUBLIC_KEY}:${SANDBOX_PRIVATE_KEY}" \
-H "X-Origin: third-party-api.mara.boo" \
-H "X-Timestamp: ${TIMESTAMP}" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json"A successful response (status 200) indicates your authentication is working correctly.
Next Steps
- API Keys Guide - Learn how to generate and manage API keys
- Environments - Understand sandbox vs production environments
- Webhooks - Set up webhooks for real-time notifications
- API Reference - Explore all available endpoints